
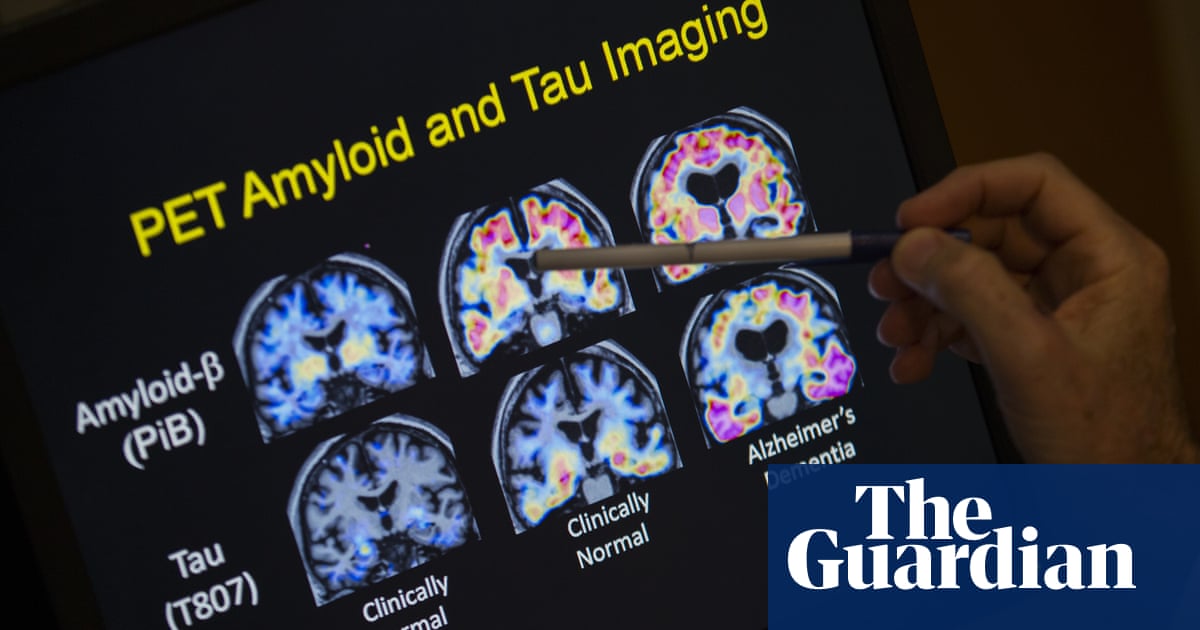
A recent study published in Nature Medicine indicates that Alzheimers disease may have a stronger genetic component than previously understood, with researchers suggesting that a distinct, inherited form of the disease exists. Familial forms of Alzheimers, caused by mutations in certain genes like APOE4, are now considered to account for about 1 in 6 cases, challenging the previous notion of the disease being mostly sporadic. The APOE gene, responsible for producing a lipid-carrying protein, plays a significant role in the development of Alzheimers, with different variants like APOE2 being protective and APOE4 increasing the risk significantly.

Apolipoprotein E (Apo-E) is a protein involved in the metabolism of fats in the body of mammals. A subtype is implicated in Alzheimer's disease and cardiovascular diseases. It is encoded in humans by the gene APOE.Apo-E belongs to a family of fat-binding proteins called apolipoproteins. In the circulation, it is present as part of several classes of lipoprotein particles, including chylomicron remnants, VLDL, IDL, and some HDL. APOE interacts significantly with the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), which is essential for the normal processing (catabolism) of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. In peripheral tissues, APOE is primarily produced by the liver and macrophages, and mediates cholesterol metabolism. In the central nervous system, Apo-E is mainly produced by astrocytes and transports cholesterol to neurons via APOE receptors, which are members of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family. Apo-E is the principal cholesterol carrier in the brain. APOE qualifies as a checkpoint inhibitor of the classical complement pathway by complex formation with activated C1q.

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens, and is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progress of the protein misfolding disease is largely associated with amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and loss of neuronal connections in the brain. A probable diagnosis is based on the history of the illness and cognitive testing, with medical imaging and blood tests to rule out other possible causes. Initial symptoms are often mistaken for normal brain aging. Examination of brain tissue is needed for a definite diagnosis, but this can only take place after death.No treatments can stop or reverse its progression, though some may temporarily improve symptoms. A healthy diet, physical activity, and social engagement are generally beneficial in ageing, and may help in reducing the risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer's. Affected people become increasingly reliant on others for assistance, often placing a burden on caregivers. The pressures can include social, psychological, physical, and economic elements. Exercise programs may be beneficial with respect to activities of daily living and can potentially improve outcomes. Behavioral problems or psychosis due to dementia are sometimes treated with antipsychotics, but this has an increased risk of early death.As of 2020, there were approximately 50 million people worldwide with Alzheimer's disease. It most often begins in people over 65 years of age, although up to 10% of cases are early-onset impacting those in their 30s to mid-60s. It affects about 6% of people 65 years and older, and women more often than men. The disease is named after German psychiatrist and pathologist Alois Alzheimer, who first described it in 1906. Alzheimer's financial burden on society is large, with an estimated global annual cost of US$1 trillion. It is ranked as the seventh leading cause of death in the United States.

Alois Alzheimer ( ALTS-hy-mər, US also AHLTS-, AWLTS-, German: [ˈaːlɔɪs ˈʔaltshaɪmɐ]; 14 June 1864 – 19 December 1915) was a German psychiatrist and neuropathologist and a colleague of Emil Kraepelin. Alzheimer is credited with identifying the first published case of "presenile dementia", which Kraepelin would later identify as Alzheimer's disease.

Alzheimer's Society is a United Kingdom care and research charity for people with dementia and their carers. It operates in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, while its sister charities Alzheimer Scotland and Alzheimer Society of Ireland cover Scotland and the Republic of Ireland respectively.Despite its name, the charity does not exclusively help people with Alzheimer's disease. There are many types of dementia, which is an umbrella term. Dementia types include vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal dementia, Korsakoff's syndrome, Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, HIV-related cognitive impairment, mild cognitive impairment, and other rarer causes of dementia.It is a organisation that provides support for people affected by dementia via a telephone support line, as well as through dementia support workers, printed information and an online community called Talking Point. Alzheimer's Society funds dementia research. In 2021/2022, £7m was given in 27 awards for new research, and 311 new publications came from their funding.The society relies on voluntary donations from the public through fundraising and other activities. It is a registered Charity No. 296645, registered as a company limited by guarantee and registered in England No. 2115499. Its registered office is at 43-44 Crutched Friars, London, EC3N 2AE.As of 2023 the Chief Executive of the Alzheimer's Society is Kate Lee, who replaced Jeremy Hughes on 2 March 2020.

Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL cholesterol), in the blood and early cardiovascular diseases. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver or produce abnormal LDL receptors that never go to the cell surface to function properly (abnormal trafficking). Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH (such as dietary modification and statin tablets). Nevertheless, treatment (including higher statin doses) is usually effective.FH is classified as a type 2 familial dyslipidemia. There are five types of familial dyslipidemia (not including subtypes), and each are classified from both the altered lipid profile and by the genetic abnormality. For example, high LDL (often due to LDL receptor defect) is type 2. Others include defects in chylomicron metabolism, triglyceride metabolism, and metabolism of other cholesterol-containing particles, such as VLDL and IDL.About 1 in 100 to 200 people have mutations in the LDLR gene that encodes the LDL receptor protein, which normally removes LDL from the circulation, or apolipoprotein B (ApoB), which is the part of LDL that binds with the receptor; mutations in other genes are rare but important to know, including gain-of-function mutations in PCSK9, the molecular "scissor" of LDL receptors, resulting in less LDLR available. PCSK9 mutations cause less than 5% of cases of FH according to most epidemiologic studies. People who have one abnormal copy (are heterozygous) of the LDLR gene may develop cardiovascular disease prematurely at the age of 30 to 40. Having two abnormal copies (being homozygous) may cause severe cardiovascular disease in childhood. Heterozygous FH is a common genetic disorder, inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, occurring in 1:250 people in most countries; homozygous FH is much rarer, occurring in 1 in 300,000 people.Heterozygous FH is normally treated with statins, bile acid sequestrants, or other lipid-lowering agents that lower cholesterol levels. New cases are generally offered genetic counseling. Homozygous FH often does not respond to medical therapy and may require other treatments, including LDL apheresis (removal of LDL in a method similar to dialysis) and occasionally liver transplantation.

The Alzheimer Case (also known as The Alzheimer Affair or The Memory of a Killer; Dutch: De zaak Alzheimer) is a 2003 Belgian action thriller film directed by Erik Van Looy, based on the novel De zaak Alzheimer by Jef Geeraerts. It follows an assassin with Alzheimer's disease, who plans to retire but ends up becoming a target himself after he refuses to kill a young girl.It was officially remade in English-language as Memory.

Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids (oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins) to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph.The lipid components of lipoproteins are insoluble in water. However, because of their detergent-like (amphipathic) properties, apolipoproteins and other amphipathic molecules (such as phospholipids) can surround the lipids, creating a lipoprotein particle that is itself water-soluble, and can thus be carried through body fluids (i.e., blood, lymph).In addition to stabilizing lipoprotein structure and solubilizing the lipid component, apolipoproteins interact with lipoprotein receptors and lipid transport proteins, thereby participating in lipoprotein uptake and clearance. They also serve as enzyme cofactors for specific enzymes involved in the metabolism of lipoproteins.Apolipoproteins are also exploited by hepatitis C virus (HCV) to enable virus entry, assembly, and transmission. They play a role in viral pathogenesis and viral evasion from neutralizing antibodies.





https://www.theguardian.com/profile/nicola-davis

ABC News

ABC News

Yahoo! News

Yahoo! News

Xantha Leatham

By LAURAN NEERGAARD

Brenda Goodman

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

Wikipedia