
TSMC's Arizona subsidiary will receive up to $6.6 billion in U.S. government funding to support its $65 billion investment in three cutting-edge fabrication plants in Phoenix, Arizona. This funding is part of the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act, with additional eligibility for around $5 billion in proposed loans. The partnership aims to bring the manufacturing of advanced chips to America, creating jobs and training local talent. The CHIPS Act, passed in August 2022, incentivizes companies to produce chips domestically to enhance the economy and national security.

The Biden administration has awarded GlobalFoundries $1.5 billion in funding to enhance domestic chip production in New York and Vermont under the $52 billion CHIPS and Science Act. This funding will support the construction of a new fabrication plant in Malta, NY, upgrading existing facilities, and creating jobs. The chips produced by GlobalFoundries are vital for military equipment, electric vehicles, smartphones, and faster internet connections for Americans. The government will also provide loans totaling $1.6 billion, with expected total investments of $12.5 billion.

The CHIPS and Science Act is a U.S. federal statute enacted by the 117th United States Congress and signed into law by President Joe Biden on August 9, 2022. The act authorizes roughly $280 billion in new funding to boost domestic research and manufacturing of semiconductors in the United States, for which it appropriates $52.7 billion. The act includes $39 billion in subsidies for chip manufacturing on U.S. soil along with 25% investment tax credits for costs of manufacturing equipment, and $13 billion for semiconductor research and workforce training, with the dual aim of strengthening American supply chain resilience and countering China.: 1 It also invests $174 billion in the overall ecosystem of public sector research in science and technology, including in NASA, the DOE, and NIST.The act does not have an official short title as a whole but is divided into three divisions with their own short titles: Division A is the CHIPS Act of 2022 (where CHIPS stands for "Creating Helpful Incentives to Produce Semiconductors"); Division B is the Research and Development, Competition, and Innovation Act; and Division C is the Supreme Court Security Funding Act of 2022.By March 2024, analysts estimated that the act incentivized between 25 to 50 separate potential projects, with total projected investments of $160-200 billion and 25,000 - 45,000 new jobs. However, these projects are faced with delays in receiving grants due to bureaucratic hurdles and shortages of skilled workers, both during the construction phase and upon completion in the operational/manufacturing stage, where 40% of the permanent new workers will need two year technician degrees and 60% will need four year engineering degrees or higher.

Samsung is planning to increase its initial $17 billion investment in Taylor, Texas to about $44 billion by constructing a second chip factory and a new facility for advanced packaging and R&D, with an official announcement expected on April 15th. This expansion aligns with President Biden's CHIPS Act, aiming to attract global chipmakers to invest in the US by providing incentives like over $6 billion to Samsung. The CHIPS Act has also supported other tech companies like GlobalFoundries and Intel, leading to significant investments in US-based chip manufacturing.

The Biden administration has announced a $5 billion investment in a public-private consortium called the National Semiconductor Technology Center, aimed at supporting research and development in advanced computer chips. The funding is part of the CHIPS and Science Act signed in 2022, which aims to reinvigorate the computer chip sector within the United States. The center will fund the design and prototyping of new chips and provide training for workers in the sector. The investment comes as the demand for advanced chips increases due to the emergence of artificial intelligence and the need to reduce dependence on foreign chip manufacturers.

President Biden is set to announce a deal with Intel that includes up to $8.5 billion in grants and $11 billion in loans to build semiconductor plants in four states. This funding is part of the CHIPS and Science Act passed by Congress in 2022 to enhance US production of electronic devices. Intel will invest over $100 billion, potentially offset by $25 billion in tax credits, creating around 30,000 jobs. The aim is to address the reliance on imports, combat price spikes, and shortages in industries like cars and appliances.

Intel's chip-making division reported operating losses of $7 billion in 2023, up from $5.2 billion in 2022, leading to a 31% decrease in revenue to $18.9 billion. The company aims to break even by 2027 after investing in extreme ultraviolet (EUV) machines. Intel plans to spend $100 billion on chip foundries in the U.S., with $8.5 billion in funding from the CHIPS Act. TSMC remains Intel's biggest competitor with a 53% gross margin compared to Intel's projected 40% margin by 2030.

Pat Gelsinger discusses the billions in U.S. grants the company received to enhance domestic manufacturing on The Claman Countdown. Semiconductor giant Intel announced Wednesday that it will receive about $20 billion in federal subsidies under the CHIPS and Science Act to advance semiconductor manufacturing projects in four U.S.

The European Chips Act (ECA), also known as simply the Chips Act, is a legislative package to encourage semiconductor production in the European Union.First announced in February 2022, the Commission has intended through the ECA to reclaim market share from the dominant Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company and reduce European exposure to supply chain risks. The ECA is part of a "Chips for Europe" investment plan which will span at least until 2030, and aims to establish Europe as "a leader in this market", according to president of the European Commission Ursula von der Leyen. The proposal has three "pillars":research, development and innovationa new state aid exemption covering semiconductor manufacturing, andmeasures to monitor the supply chain and intervene if necessary.As of 2022, Europe accounts for less than 10 percent of the production of semiconductors worldwide, and the Commission hopes to increase the figure to 20 percent with a 43 billion euro investment.A political agreement was found in the Spring of 2023 and the Chips Act (Regulation (EU) 2023/1781 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 September 2023 establishing a framework of measures for strengthening Europe’s semiconductor ecosystem and amending Regulation (EU) 2021/694) was published in the Official Journal of the EU on 18 September 2023.

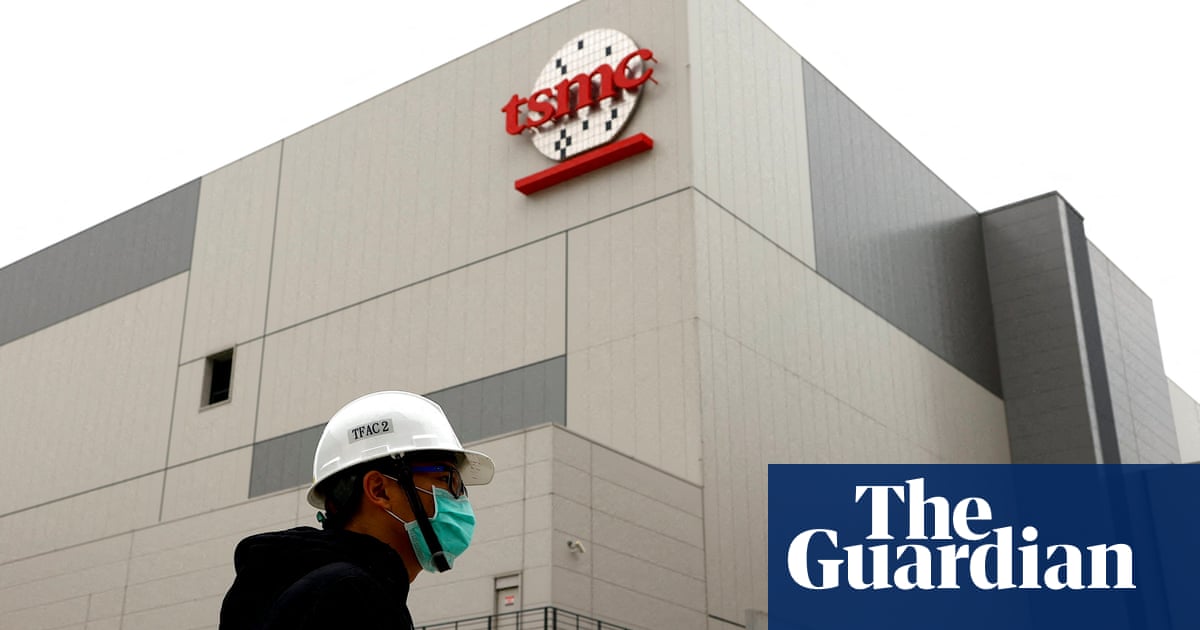
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC; also called Taiwan Semiconductor) is a Taiwanese multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the world's second most valuable semiconductor company, the world's largest dedicated independent ("pure-play") semiconductor foundry, and its country's largest company, with headquarters and main operations located in the Hsinchu Science Park in Hsinchu, Taiwan. It is majority owned by foreign investors, and the central government of Taiwan is the largest shareholder. In 2023, the company was ranked 44th in the Forbes Global 2000.Taiwan's exports of integrated circuits amounted to $184 billion in 2022, accounted for nearly 25 percent of Taiwan's GDP. TSMC accounts for about 30 percent of the Taiwan Stock Exchange's main index.TSMC was founded in Taiwan in 1987 by Morris Chang as the world's first dedicated semiconductor foundry. It has long been the leading company in its field. When Chang retired in 2018, after 31 years of TSMC leadership, Mark Liu became chairman and C. C. Wei became Chief Executive. It has been listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange (TWSE: 2330) since 1993; in 1997 it became the first Taiwanese company to be listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE: TSM). Since 1994, TSMC has had a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.4% in revenue and a CAGR of 16.1% in earnings.Most of the leading fabless semiconductor companies such as AMD, Apple, ARM, Broadcom, Marvell, MediaTek, Qualcomm and Nvidia, are customers of TSMC, as are emerging companies such as Allwinner Technology, HiSilicon, Spectra7, and UNISOC. Leading programmable logic device companies Xilinx and previously Altera also make or made use of TSMC's foundry services. Some integrated device manufacturers that have their own fabrication facilities, such as Intel, NXP, STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments, outsource some of their production to TSMC. At least one semiconductor company, LSI, re-sells TSMC wafers through its ASIC design services and design IP portfolio.TSMC has a global capacity of about thirteen million 300 mm-equivalent wafers per year as of 2020 and makes chips for customers with process nodes from 2 microns to 3 nanometres. TSMC was the first foundry to market 7-nanometre and 5-nanometre (used by the 2020 Apple A14 and M1 SoCs, the MediaTek Dimensity 8100, and AMD Ryzen 7000 series processors) production capabilities, and the first to commercialize extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography technology in high volume.

In semiconductor manufacturing, the "7 nm" process is a marketing term for the MOSFET technology node following the "10 nm" node, defined by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors. It is based on FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) technology, a type of multi-gate MOSFET technology.The phrase "7 nm" does not refer to any dimension on the integrated circuits, and has no relation to gate length, metal pitch, or gate pitch; since at least 1997, "node" has become a commercial name for marketing purposes that indicates new generations of process technologies, without any relation to physical properties. However, the smallest dimension within an individual transistor, the fin width, can sometimes be 7 nm. TSMC and Samsung's "10 nm" (10 LPE) processes are somewhere between Intel's "14 nm" and "10 nm" processes in transistor density.Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) began production of 256 Mbit SRAM memory chips using a "7 nm" process called N7 in June 2016, before Samsung began mass production of their "7 nm" process called 7LPP devices in 2018. The first mainstream "7 nm" mobile processor intended for mass market use, the Apple A12 Bionic, was released at Apple's September 2018 event. Although Huawei announced its own "7 nm" processor before the Apple A12 Bionic, the Kirin 980 on August 31, 2018, the Apple A12 Bionic was released for public, mass market use to consumers before the Kirin 980. Both chips were manufactured by TSMC.In 2019, AMD released their "Rome" (EPYC 2) processors for servers and datacenters, which are based on TSMC's N7 node and feature up to 64 cores and 128 threads. They also released their "Matisse" consumer desktop processors with up to 16 cores and 32 threads. However, the I/O die on the Rome multi-chip module (MCM) is fabricated with the GlobalFoundries' 14 nm (14HP) process, while the Matisse's I/O die uses the GlobalFoundries' "12 nm" (12LP+) process. The Radeon RX 5000 series is also based on TSMC's N7 process.

An integrated circuit, also known as a microchip, chip or IC, is a small electronic device made up of multiple interconnected electronic components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors. These components are etched onto a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and televisions, to perform various functions such as processing and storing information. They have greatly impacted the field of electronics by enabling device miniaturization and enhanced functionality.Integrated circuits are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete components, allowing a large transistor count.The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design have ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones, and other home appliances are now essential parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer processors and microcontrollers.Very-large-scale integration was made practical by technological advancements in semiconductor device fabrication. Since their origins in the 1960s, the size, speed, and capacity of chips have progressed enormously, driven by technical advances that fit more and more transistors on chips of the same size – a modern chip may have many billions of transistors in an area the size of a human fingernail. These advances, roughly following Moore's law, make the computer chips of today possess millions of times the capacity and thousands of times the speed of the computer chips of the early 1970s.ICs have three main advantages over circuits constructed out of discrete components: size, cost and performance. The size and cost is low because the chips, with all their components, are printed as a unit by photolithography rather than being constructed one transistor at a time. Furthermore, packaged ICs use much less material than discrete circuits. Performance is high because the IC's components switch quickly and consume comparatively little power because of their small size and proximity. The main disadvantage of ICs is the high initial cost of designing them and the enormous capital cost of factory construction. This high initial cost means ICs are only commercially viable when high production volumes are anticipated.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25378671/image__12_.png)





https://www.theguardian.com/profile/jasper-jolly
Washington Post

ABC News

ABC News

The Verge

https://apnews.com/author/will-weissert

NBC

Business Insider

Kate Park

Sam Fossum, Anna Cooban

PANORA

Wikipedia

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

Wikipedia