
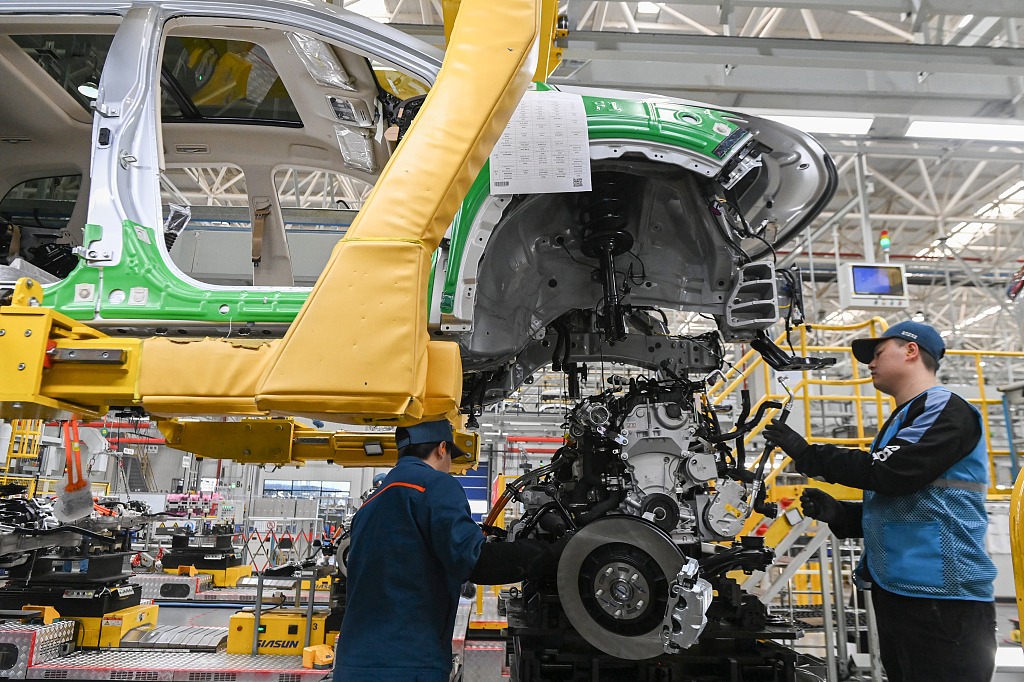
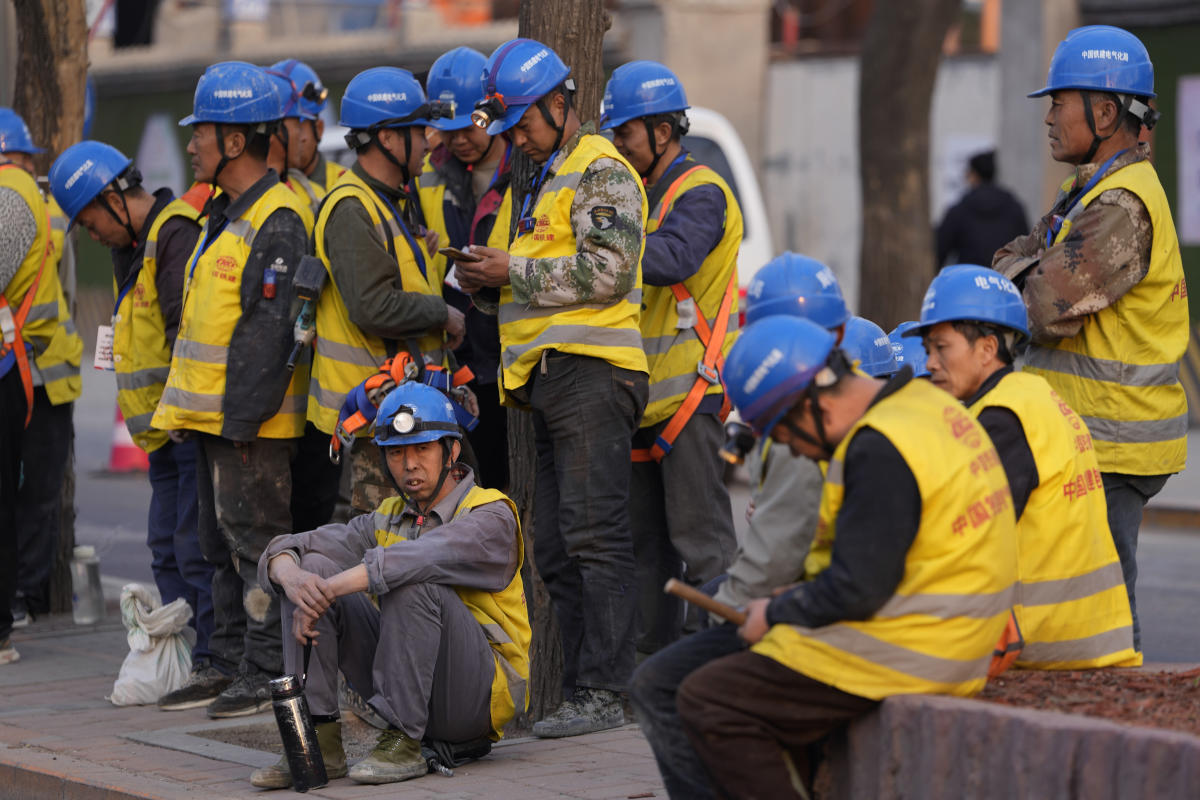
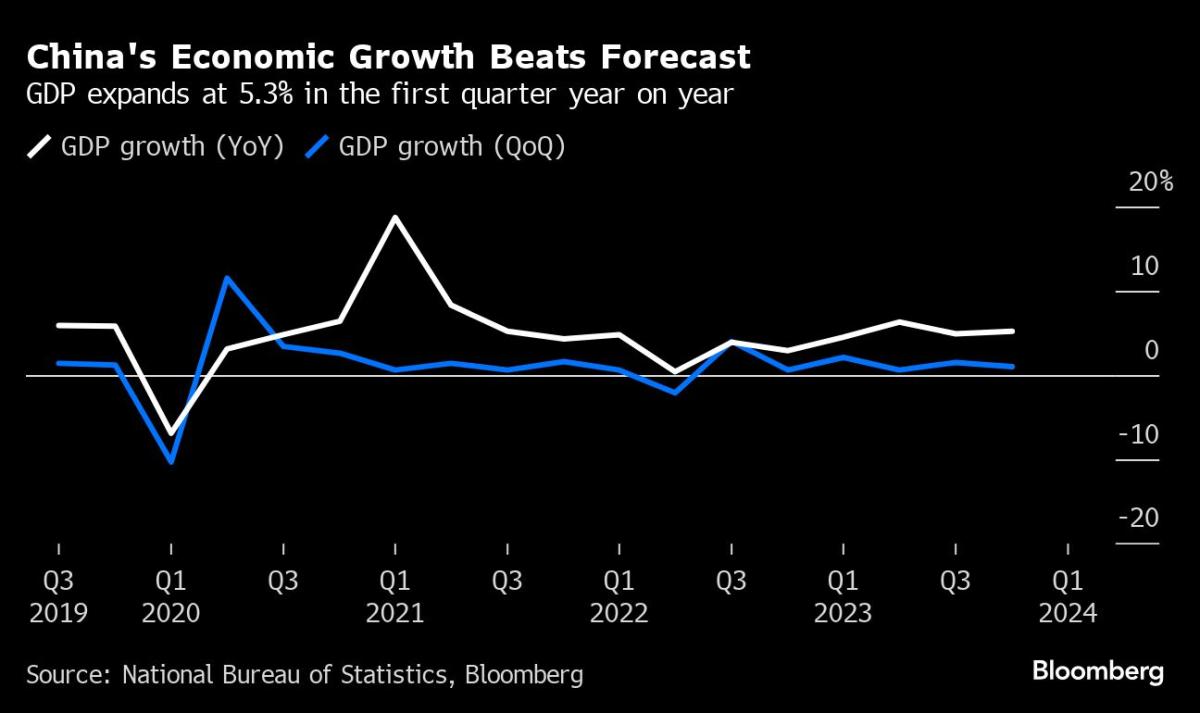
China's gross domestic product grew by 5.3% in the first quarter of 2024, beating the estimated 4.6% growth. Factory activity has been robust, with an increase in manufacturing purchasing managers index (PMI) and overseas demand. China has set an annual growth target of around 5% for 2024 amidst weak consumer and business confidence and a downturn in the real estate sector. Authorities are implementing measures like interest rate cuts to boost bank lending and infrastructure investment.

China's Belt and Road Initiative, launched in 2013, is a public good that is aimed at addressing global inequality through mutual benefit cooperation, fair market integration and the development of infrastructure, mainly in the Global South. Nowadays, with prevalent protectionism worldwide, China, through the BRI, is promoting free trade, multilateralism and globalization. The initiative also bolsters cultural and diplomatic links, as well as friendship among peoples worldwide. The BRI has expanded from China's neighboring countries, not only along the ancient overland Silk Road routes, but also through new maritime ways connecting China with countries in Southeast Asia, Europe, Latin America, Africa and the Middle East. Infrastructure plays an important role in the BRI.

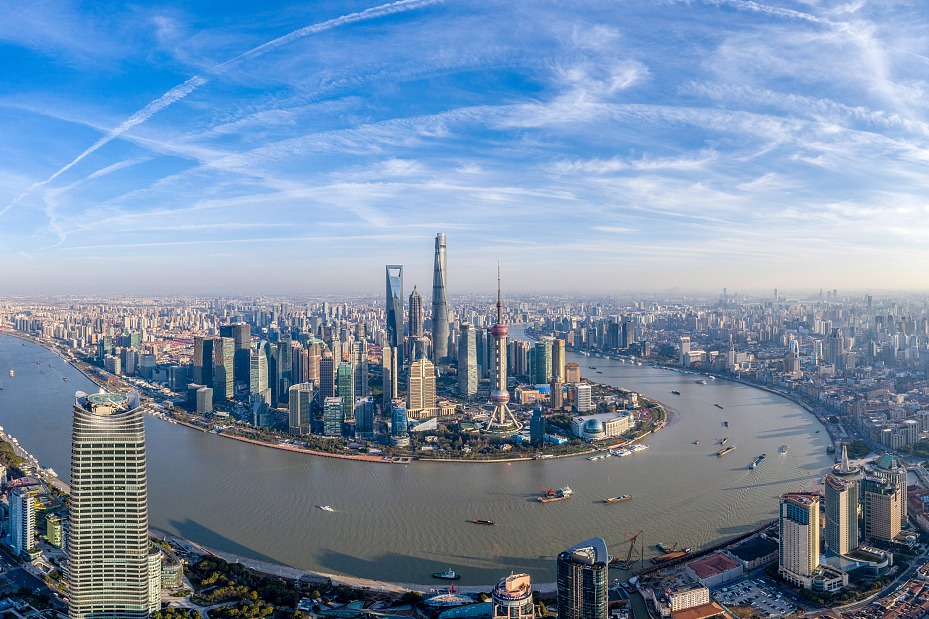
China (Chinese: 中国; pinyin: Zhōngguó), officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the world's second-most-populous country. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land. With an area of nearly 9.6 million square kilometers (3,700,000 sq mi), it is the third-largest country by total land area. The country is divided into 33 province-level divisions, inclusive of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the national capital, while Shanghai is the most populous city and largest financial center.The region has been inhabited since the Paleolithic era. Early Chinese dynasties, such as the Xia, Shang and the Zhou, emerged in the basin of the Yellow River before the late second millennium BCE. The eighth to third centuries BCE saw a breakdown in Zhou authority and significant conflict, as well as the emergence of literature, philosophy, and historiography. In 221 BCE, China was unified under an emperor for the first time. Appointed non-hereditary officials began ruling counties instead of the aristocracy, ushering in more than two millennia of imperial dynasties including the Qin, Han, Tang, Yuan, Ming, and Qing. With the invention of gunpowder and paper, the establishment of the Silk Road, and the building of the Great Wall, Chinese culture—including languages, traditions, architecture, philosophy and more—flourished and has heavily influenced East Asia and beyond.In 1912, after decades of struggle, the monarchy was overthrown and the Republic of China (ROC) was established. Despite victory in the Second Sino-Japanese War, the Asian Pacific theater of World War II, numerous atrocities such as the Nanjing Massacre left lasting effects on the country. The Soviet-backed Chinese Communist Party (CCP) fought the US-backed Kuomintang government on-and-off since 1927. In 1949 the CCP established control over most of the territory of the republic. As the Kuomintang retreated to Taiwan, the country is split with both sides claiming to be the sole legitimate government. After the land reform, later attempts to realize communism failed miserably: the Great Leap Forward led to massive famine, while the Cultural Revolution caused a chaotic period of persecution and zealous populism. Following the Sino-Soviet split, the Shanghai Communiqué in 1972 marked the beginning of normalization of China-American relationship. Economic reforms that begin in 1978 moved the country away from planned economy toward an increasingly open market economy, while political reforms stalled after the June Fourth Incident in 1989.China is a unitary one-party socialist republic led by the CCP. It is a founding member of the United Nations (UN) and one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council. It is a founding member of several multilateral and regional organizations such as the AIIB, the Silk Road Fund, the New Development Bank, and the RCEP. It is a member of the BRICS, the G20, APEC, the SCO, and the East Asia Summit. Making up around one-fifth of the world economy, China is the world's largest economy by GDP at purchasing power parity, the second-largest economy by nominal GDP, and the second-wealthiest country, albeit ranking poorly in measures of democracy and human rights. The country has been one of the fastest-growing major economies and is the world's largest manufacturer and exporter, as well as the second-largest importer. China is a nuclear-weapon state with the world's largest standing army by military personnel and the second-largest defense budget. It is a great power and a regional power.






Business Insider

ABC News

ABC News

ABC News

ABC News

Yahoo! News

Yahoo! News

Yahoo! News

于小明

马清

https://apnews.com/author/zen-soo

Laura He

Yahoo! News

Yahoo! News

https://www.facebook.com/bbcnews

Al Jazeera

NBC

Fox News

PANORA

Wikipedia