
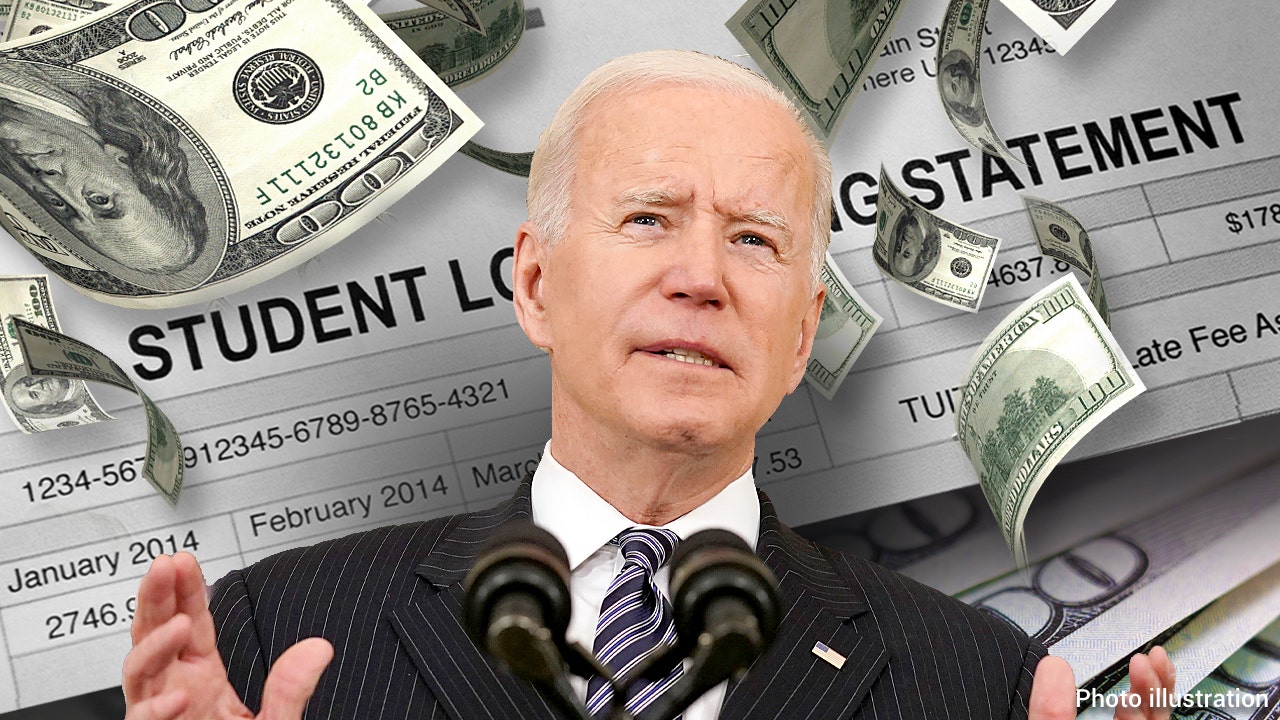
President Biden has announced the cancellation of $7.4 billion in student debt for more than 277,000 individuals as part of his ongoing efforts to address student loan burdens. This move follows previous debt cancellation initiatives totalling $153 billion for 4.3 million borrowers. The relief will be distributed in three categories, with impacted individuals to be notified via email starting from Friday. The Biden administration aims to fulfil campaign promises and provide debt relief to as many Americans as possible through various approaches, after facing setbacks in previous attempts to cancel larger amounts of student debt.

The Biden administration revealed a new plan to eliminate student debt for over 30 million borrowers, offering targeted relief to specific groups like long-time debt holders and those struggling to make payments. The plan includes forgiving up to $20,000 in interest for any borrower, irrespective of income, and completely forgiving interest for low and middle-income borrowers in income-driven repayment plans.

Republican-led states, including Missouri, Kansas, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, North Dakota, Ohio, and Oklahoma, are suing the Biden administration over the student loan forgiveness program called the SAVE plan, arguing that the President lacks the authority to unilaterally cancel student loan debt without Congress. The program, which aims to reduce monthly payments and provide forgiveness after 10 to 25 years, has faced legal challenges despite forgiving $1.2 billion in debt for 153,000 borrowers in February. The Biden administration, confident in the new plan, hopes to cancel debt for up to 25 million borrowers, potentially costing up to $500 billion if each borrower receives an average forgiveness of $20,000.

Joe Biden's tenure as the 46th president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 2021. Biden, a Democrat from Delaware who previously served as vice president for two terms under President Barack Obama, took office following his victory in the 2020 presidential election over Republican incumbent president Donald Trump. Upon his inauguration, he became the oldest president in American history, breaking the record set by his predecessor Trump. Biden entered office amid the COVID-19 pandemic, an economic crisis, and increased political polarization.On the first day of his presidency, Biden made an effort to revert President Trump's energy policy by restoring U.S. participation in the Paris Agreement and revoking the permit for the Keystone XL pipeline. He also halted funding for Trump's border wall, an expansion of the Mexican border wall. On his second day, he issued a series of executive orders to reduce the impact of COVID-19, including invoking the Defense Production Act of 1950, and set an early goal of achieving one hundred million COVID-19 vaccinations in the United States in his first 100 days.Biden signed into law the American Rescue Plan Act of 2021; a $1.9 trillion stimulus bill that temporarily established expanded unemployment insurance and sent $1,400 stimulus checks to most Americans in response to continued economic pressure from COVID-19. He signed the bipartisan Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act; a ten-year plan brokered by Biden alongside Democrats and Republicans in Congress, to invest in American roads, bridges, public transit, ports and broadband access. Biden signed the Juneteenth National Independence Day Act, making Juneteenth a federal holiday in the United States. He appointed Ketanji Brown Jackson to the U.S. Supreme Court—the first Black woman to serve on the court. After The Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade, Biden took executive actions, such as the signing of Executive Order 14076, to preserve and protect women's health rights nationwide, against abortion bans in Republican led states. Biden proposed a significant expansion of the U.S. social safety net through the Build Back Better Act, but those efforts, along with voting rights legislation, failed in Congress. However, in August 2022, Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, a domestic appropriations bill that included some of the provisions of the Build Back Better Act after the entire bill failed to pass. It included significant federal investment in climate and domestic clean energy production, tax credits for solar panels, electric cars and other home energy programs as well as a three-year extension of Affordable Care Act subsidies. Biden signed the CHIPS and Science Act, bolstering the semiconductor and manufacturing industry, the Honoring our PACT Act, expanding health care for US veterans, and the Electoral Count Reform and Presidential Transition Improvement Act. In late 2022, Biden signed the Respect for Marriage Act, which repealed the Defense of Marriage Act and codified same-sex and interracial marriage in the United States. In response to the debt-ceiling crisis of 2023, Biden negotiated and signed the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023, which restrains federal spending for fiscal years 2024 and 2025, implements minor changes to SNAP and TANF, includes energy permitting reform, claws back some IRS funding and unspent money for COVID-19, and suspends the debt ceiling to January 1, 2025. Biden established the American Climate Corps and created the first ever White House Office of Gun Violence Prevention. On September 26, 2023, Joe Biden visited a United Auto Workers picket line during the 2023 United Auto Workers strike, making him the first US president to visit one.The foreign policy goal of the Biden administration is to restore the US to a "position of trusted leadership" among global democracies in order to address the challenges posed by Russia and China. In foreign policy, Biden completed the withdrawal of U.S. military forces from Afghanistan, declaring an end to nation-building efforts and shifting U.S. foreign policy toward strategic competition with China and, to a lesser extent, Russia. However, during the withdrawal, the Afghan government collapsed and the Taliban seized control, leading to Biden receiving bipartisan criticism. He responded to the Russian invasion of Ukraine by imposing sanctions on Russia as well as providing Ukraine with over $100 billion in combined military, economic, and humanitarian aid. Biden also approved a raid which led to the death of Abu Ibrahim al-Hashimi al-Qurashi, the leader of the Islamic State, and approved a drone strike which killed Ayman Al Zawahiri, leader of Al-Qaeda. Biden signed AUKUS, an international security alliance, together with Australia and the United Kingdom. Biden called for the expansion of NATO with the addition of Finland and Sweden, and rallied NATO allies in support of Ukraine. During the Israel–Hamas war, Biden condemned Hamas and other Palestinian militants as terrorism and announced American military support for Israel; Biden also showed his support and sympathy towards Palestinians affected by the war, sent humanitarian aid, and brokered a four-day temporary pause and hostage exchange.Biden began his term with over 50% approval ratings; however, these fell significantly after the withdrawal from Afghanistan and remained low as the country experienced high inflation and rising gas prices. His age and mental fitness have also been a subject of discussion.

Joseph Robinette Biden Jr. ( , BY-dən; born November 20, 1942) is an American politician who is the 46th and current president of the United States. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 47th vice president from 2009 to 2017 under President Barack Obama and represented Delaware in the United States Senate from 1973 to 2009.Born in Scranton, Pennsylvania, Biden moved with his family to Delaware in 1953. He graduated from the University of Delaware before earning his law degree from Syracuse University. He was elected to the New Castle County Council in 1970 and to the U.S. Senate in 1972. As a senator, Biden drafted and led the effort to pass the Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act and the Violence Against Women Act. He also oversaw six U.S. Supreme Court confirmation hearings, including the contentious hearings for Robert Bork and Clarence Thomas. Biden ran unsuccessfully for the Democratic presidential nomination in 1988 and 2008. In 2008, Obama chose Biden as his running mate, and he was a close counselor to Obama during his two terms as vice president. In the 2020 presidential election, Biden and his running mate, Kamala Harris, defeated incumbents Donald Trump and Mike Pence. He is the oldest president in U.S. history, and the first to have a female vice president.As president, Biden signed the American Rescue Plan Act in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent recession. He signed bipartisan bills on infrastructure and manufacturing. He proposed the Build Back Better Act, which failed in Congress, but aspects of which were incorporated into the Inflation Reduction Act that he signed into law in 2022. Biden appointed Ketanji Brown Jackson to the Supreme Court. He worked with congressional Republicans to resolve the 2023 United States debt-ceiling crisis by negotiating a deal to raise the debt ceiling. In foreign policy, Biden restored America's membership in the Paris Agreement. He oversaw the complete withdrawal of U.S. troops from Afghanistan that ended the war in Afghanistan, during which the Afghan government collapsed and the Taliban seized control. He responded to the Russian invasion of Ukraine by imposing sanctions on Russia and authorizing civilian and military aid to Ukraine. During the Israel–Hamas war, Biden announced military support for Israel, and condemned the actions of Hamas and other Palestinian militants as terrorism. In April 2023, Biden announced his candidacy for the Democratic nomination in the 2024 presidential election.

White House press secretary Karine Jean-Pierre defended President Biden's remarks accusing House Republicans of 'killing millions of Americans' by slashing the Affordable Care Act. Jean-Pierre emphasized the importance of affordable health care and criticized Republicans for repealing the act despite its life-saving impact. The discussion with Fox News' Jacqui Heinrich highlighted differing interpretations of Biden's language, with Jean-Pierre insisting that the president was aiming to protect Americans' health care. Trump's contrasting views on Obamacare were also mentioned, with his intention to make ACA 'much better' if re-elected.

The US consumer price index (CPI) rose 3.5 percent in March from a year earlier, higher than predicted, leading economists to doubt the Federal Reserve will cut interest rates this year. Stock prices fell and bond yields rose after the CPI report, impacting President Biden's approval ratings. Core prices also increased more than expected. Despite the inflation surge, the US economy appears solid with low unemployment rates. Analysts, like those at Goldman Sachs, have revised rate-cut predictions multiple times due to unpredictable inflation patterns and market reactions.

President Biden responds to Arizona's Supreme Court ruling allowing enforcement of a 1864 abortion ban, stating that the law belongs to an era not reflective of the current times. Biden's re-election campaign launches a media blitz in Arizona, countering former President Trump's stance on abortion and aiming to reach key voters. The campaign highlights the impact of Trump's policies on women's reproductive rights and vows to fight for freedom of choice. Vice President Kamala Harris plans to address reproductive freedom during a visit to Arizona, focusing on Trump's role in abortion policy.








Business Insider

NY Post
Washington Post

ABC News

Sarah Ewall-Wice

https://apnews.com/author/collin-binkley

Fox News

Fox News

https://www.facebook.com/bbcnews

PANORA

PANORA

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA