
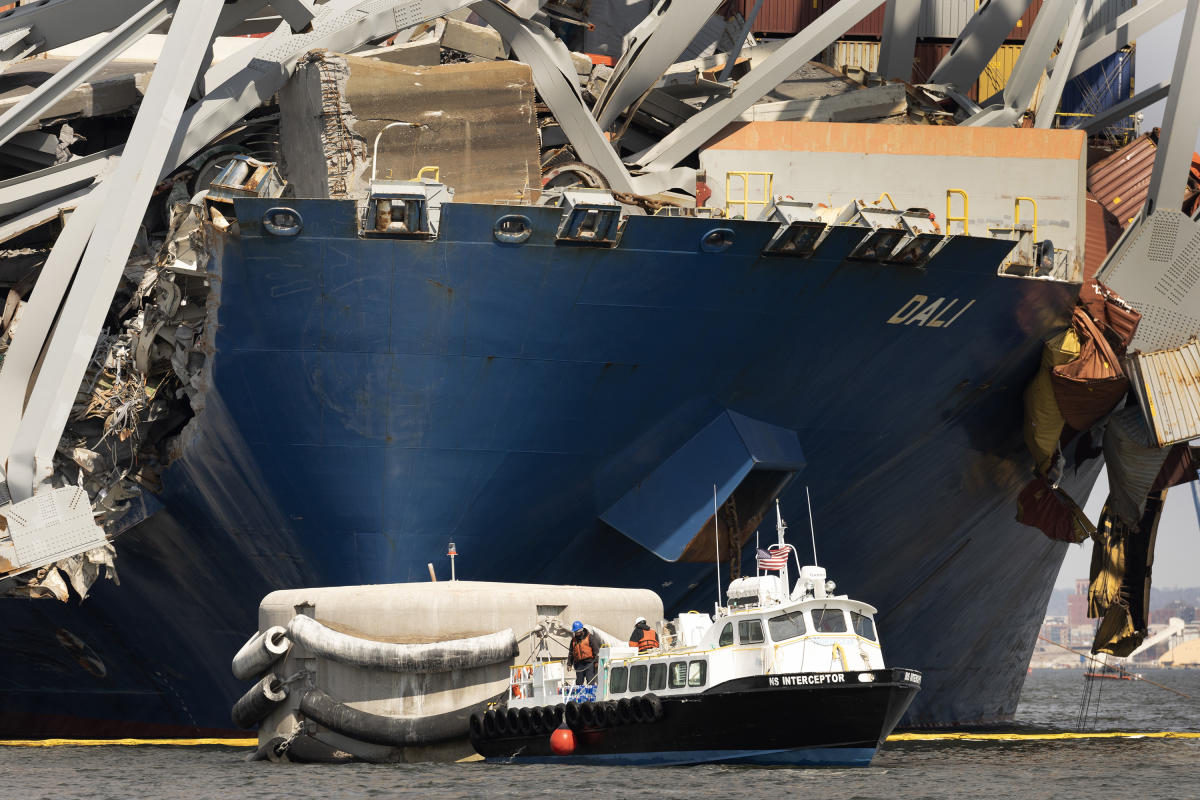
Authorities in Baltimore are working to clean up the debris in the Patapsco River after a 984-foot ship collided with the Francis Scott Key Bridge, causing it to collapse and killing six construction workers, with only two bodies recovered so far. Salvage efforts involve cutting up the bridge, refloating the ship, and removing wreckage, albeit facing challenges like unsafe diving conditions. The process, similar to a past incident in Georgia, is expected to be time-intensive, but aims to reopen the shipping channel and aid in future salvage operations.

A massive floating crane capable of lifting 1,000 tons at once has arrived at the site of the collapsed Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, Maryland. The bridge wreckage, weighing upwards of 4,000 tons, rests on the cargo ship Dali and will need to be cut into four parts for removal. Federal resources are being allocated to Maryland to address the incident and reopen the main shipping channel amidst challenges in clearing the debris from the bridge.

A ship carrying a giant crane is on its way to help clear the debris of the Francis Scott Key Bridge after it collapsed into the Patapsco River, closing the entrance to the Port of Baltimore. Four men, all Latin American immigrants, are still missing and believed to have been killed in the incident. Recovery efforts were halted due to safety concerns. The community is mourning the loss, with the Baltimore mayor's Office of Immigrant Affairs setting up a relief fund for the victims' families.

The Francis Scott Key Bridge collapse in Maryland resulted from a large container ship striking a support column, causing vehicles to plunge into the Patapsco River. Carnival Corporation forecasts a negative impact of up to $10 million on its 2024 earnings due to the incident, leading to disruptions in vessel traffic at the Port of Baltimore. Cargo bound for Baltimore may be diverted to the Port of New York and New Jersey, with potential supply chain disruptions affecting businesses, particularly in the automotive industry.

The Singapore-flagged container ship, Dali, collided with Baltimore's Key Bridge, causing it to collapse, with previous history of crashing into a dock in Antwerp, Belgium in 2016. The 948-feet-long vessel was enroute to Colombo from Baltimore and has a capacity of 111,000 tonnes. The incident led to a rescue operation as cars and construction workers fell into the Patapsco River. The ship's crew, all Indian nationals, were questioned by the Coast Guard. The bridge collapse caused a mass casualty event with ongoing search and rescue efforts.

The Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore partially collapsed into the Patapsco River after a freighter crashed into it, causing significant damage. The steel-arched bridge, built in the 1970s, was considered an engineering feat. The incident resulted in a structural failure of the bridge.

On March 26, 2024, at 01:28 EDT (05:28 UTC), part of the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, Maryland, United States, collapsed after the container ship Dali struck one of its support pillars.Baltimore City Fire Department stated that at least seven vehicles fell into the water. Two people were recovered from the river; one was not injured while the other was transported to hospital in critical condition, and at least seven people are believed missing.

The collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore has suspended vessel traffic at the Port of Baltimore, affecting trade and supply chains. Maryland has received $60 million in federal funding for debris recovery. The incident involved the Dali, a Singapore-registered ship heading to Sri Lanka. The port handles various cargo, including automobiles and coal exports. While vessel traffic is halted, trucks are still moving within the terminals, impacting the ninth-largest US port's operations.

The bodies of Alejandro Hernandez Fuentes from Mexico and Dorlian Ronial Castillo Cabrera from Guatemala have been recovered from a red pick-up truck in the Patapsco River after the Frances Scott Key Bridge collapsed. Four people are still missing and presumed dead, with recovery efforts suspended due to dangerous conditions. The victims, part of a crew filling potholes on the bridge, included workers from Mexico, Honduras, El Salvador, and Guatemala. Sonar vehicles indicate the remaining vehicles are likely encased in concrete from the collapsed structures.

A massive cargo ship lost power, leading to a crash with the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, resulting in the bridge collapsing into the Patapsco River. Two construction workers were found dead, and four are presumed dead. The Baltimore port's closure will impact the city's economy and the country's supply chain. President Biden approved a $60 million federal aid request for emergency costs. Maryland Governor called for citizen support in rebuilding efforts. The port's closure affects the automobile industry, with some automakers rerouting shipments.

The collapse of Baltimore's Francis Scott Key Bridge disrupts the supply chain and port operations, causing chaos for the shipping industry. The Port of Baltimore, generating $2.6 billion in business income annually, is shut down indefinitely, impacting $80.8 billion worth of foreign cargo. Experts estimate a loss of over $15 million in local economic activity daily as ships wait in Chesapeake Bay for rerouting instructions.

The reconstruction of Baltimore's collapsed Francis Scott Key Bridge could last 18 months to several years with costs estimated at $400 million or more. Factors affecting the timeline include design, permit approvals, and contract awards. Experts predict the project could take five to seven years, with contrasting views on how quickly it can be completed. The recent collapse killed six workers, leading to port closures. Similar instances like Florida's Sunshine Skyway and Minnesota's I-35W bridge provide context for potential reconstruction timelines.

A cargo ship crashed into the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, causing it to collapse and kill six construction workers. The incident highlighted the specialized role of ship pilots who navigate massive ships in and out of Baltimore's port with minimal clearance. Despite the quick actions of the pilots, experts believe there was little they could do to prevent the collision. Ship pilots are highly trained local knowledge experts who play a crucial role in ensuring the safe passage of large ships carrying hazardous materials, such as oil, through challenging waterways like the Chesapeake Bay.

The collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore will have significant economic repercussions, affecting thousands of business owners, disrupting tax revenue collection, and impacting the local and state governments as well as the rest of the country. The Port of Baltimore, the busiest in the U.S. for car shipments and handling farm machinery, faces challenges with exports and imports due to the bridge collapse. Experts warn of long-lasting economic effects and disruptions in supply chains, including implications for coal producers in West Virginia.

The cargo ship Dali collided with the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore on Tuesday, March 26, 2024, causing significant damage. Efforts to remove the wreckage involved barges with cranes and a Chesapeake 1000 crane. Maryland Governor Wes Moore spoke at a news conference at Tradepoint Atlantic in Sparrows Point, Maryland on Friday, March 29, 2024, regarding the incident.

The collapse of a Baltimore bridge due to a cargo ship strike has highlighted the significance of bridges in American daily life. Six construction workers are presumed dead, and 30,000 daily drivers must find alternate routes. The closure impacts businesses and halts shipments at the Port of Baltimore. Over 42,400 US bridges are in poor condition, with aging structural components. Substructures and superstructures of these bridges are major concerns. More than 15,800 poor bridges were also in poor shape a decade ago, indicating ongoing infrastructure challenges.

Francis Scott Key Bridge, Key Bridge, or FSK Bridge can refer to:Francis Scott Key Bridge (Baltimore), a bridge that previously carried Interstate 695, which crossed the outer harbor of Baltimore, MarylandFrancis Scott Key Bridge collapse, a 2024 incident involving the Baltimore bridgeFrancis Scott Key Bridge (Washington), a bridge carrying U.S. Route 29 which crosses the Potomac River between Washington, DC and Arlington, Virginia

Maryland will receive federal emergency relief funds for the Francis Scott Key Bridge recovery mission, with an initial payment of $60 million requested for early recovery and cleanup. Federal agencies will cover the full cost of clearing shipping lanes in the Patapsco River. Maryland's congressional delegation plans to introduce legislation for more federal dollars to cover any financial gap. President Biden advocates for the federal government to pay for the full restoration of the waterway and bridge. Senators Van Hollen and Cardin intend to introduce legislation to ensure the federal government covers the full costs of the new bridge design and construction.

The Helen Delich Bentley Port of Baltimore is a shipping port along the tidal basins of the three branches of the Patapsco River in Baltimore, Maryland on the upper northwest shore of the Chesapeake Bay. It is the nation's largest port facility for specialized cargo (roll-on/roll-off ships) and passenger facilities. It is operated by the Maryland Port Administration (MPA), a unit of the Maryland Department of Transportation.During a 2006 celebration of the port's 300th birthday, the port was renamed in honor of Helen Delich Bentley (1923–2016), a former longtime U.S. Representative (Congresswoman) to the United States Congress (1985–1995) from Baltimore. She was also a former maritime reporter/editor for The Baltimore Sun, a local major daily newspaper.As of March 28, 2024, ship access to the port is blocked due to the collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge, however truck access remains open.

The Fishing Wars Memorial Bridge in Washington, previously reopened with a new span, is now closed due to concerns about its vintage section. The closure, like that of the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, highlights the challenges of aging infrastructure. Approximately 42,400 US bridges are in poor condition, with issues in their support structures. The closure of the Interstate 195 bridge in Rhode Island last year exemplifies the urgent need for infrastructure maintenance, with replacement costs estimated at $300 million. These incidents underscore a national struggle with infrastructure upkeep.

A debate has emerged over whether modern safety protections could have saved a Baltimore bridge after it was struck by a cargo ship When a 900-foot container ship struck the San FranciscoOakland Bay Bridge in 2007, the span stood firm and no one died, either on the ship or the highway above. The bridge's supports were protected by a fendering system of concrete and other materials that was installed to absorb such strikes. And it's now prompting the question: Could such a system or others like it have saved Baltimores Francis Scott Key Bridge? Some experts are saying yes. Sherif El-Tawil, a University of Michigan engineering professor, said there are several safety measures that would have made a huge difference had they been in place Tuesday morning when a cargo ship plowed into the bridge and caused its collapse. El-Tawil said a fendering system may have softened the 985-foot-long ship's blow.

The video of the Francis Scott Key Bridges collapse now exists as a global icon, giving several billion people a seemingly intimate and shocking memory of a bridge they may never have seen or heard of until social media and journalism made it ubiquitous. The video is fascinating, terrifying, mesmerizing, and it may confirm superstitions we often feel about things beyond our individual comprehension. How is it that airplanes stay up in the air, and tunnels dont collapse under the weight of water and earth? Even the most agnostic brains will make quiet and reflexive supplication for protection before crossing a bridge as dramatic as the one that collapsed this week. The loss of the bridge is first a human tragedy, for those injured or killed by its collapse. And then it is an economic shock, with a radiating toll that wont be fully understood for years , and perhaps decades.

House Rules Committee Chairman Tom Cole, R-Okla, anticipates a funding package to aid with the Francis Scott Key Bridge collapse in Baltimore will start to form in a matter of weeks. The collapse occurred after a barge struck the bridge, leading to its destruction and temporary shutdown of the Port of Baltimore. Potential damages include not only the bridge reconstruction but also the impact on port traffic. Congress is discussing its role in the situation and stands ready to collaborate with federal and state authorities.

The Francis Scott Key Bridge, known originally as the Outer Harbor Crossing until it was renamed in 1976, while still under construction, or simply as the Key Bridge or Beltway Bridge, was a steel arch continuous through truss bridge spanning the lower Patapsco River and outer Baltimore Harbor / Port carrying Maryland Route 695 in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. The main span of 1,200 feet (366 m) was the third longest span of any continuous truss in the world. It was the second-longest bridge in the Baltimore metropolitan area, after the Chesapeake Bay Bridge. On March 26, 2024, at 01:28 a.m. EDT (UTC–4), the bridge partially collapsed after the Singapore-flagged container ship Dali collided with one of its support pillars.The bridge was opened on March 23, 1977, named for amateur poet Francis Scott Key (1779–1843), the author of the American national anthem, "The Star-Spangled Banner". The bridge was the outermost of three toll crossings of Baltimore's Harbor, two tunnels and one bridge. Upon completion, the bridge structure and its approaches became the final links in Interstate 695, the "Baltimore Beltway", completing a two decades long project. Despite the I-695 signage, the bridge was officially considered part of the state highway system and designated Maryland Route 695.The bridge was 8,636 feet (2,632 m) long and carried an estimated 11.5 million vehicles annually. It was a designated hazardous materials truck route, as HAZMATs are prohibited in the Baltimore Harbor and Fort McHenry tunnels.The Key Bridge was a toll facility operated by the Maryland Transportation Authority (MDTA). As of July 1, 2013, the toll rate for cars was $4.00. The bridge was part of the E-ZPass system and included two dedicated E-ZPass lanes in its toll plaza in both the northbound and southbound directions. In April 2019, MDTA announced that the bridge would become a cashless toll facility by October 2019. With this system, customers without E-ZPass would pay using video tolling. Cashless tolling began on the bridge on October 30, 2019.The bridge was partially destroyed on March 26, 2024 when the container ship Dali crashed into a support pillar, leading to the complete failure of the bridge's center span.

The Key Bridge, is a six-lane reinforced concrete arch bridge conveying U.S. Route 29 (US 29) traffic across the Potomac River between the Rosslyn neighborhood of Arlington County, Virginia, and the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. Completed in 1923, it is Washington's oldest surviving road bridge across the Potomac River.Key Bridge was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1996.

The Dali cargo ship refueled in the Chinese cities of Zhangzhou and Zhoushan, as well as in Busan, South Korea, before heading to the East Coast of the United States. Investigators are looking into fuel as a factor in the power failure that led to the ship crashing into the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore. The data from the UN's LRIT system and MarineTraffic confirms the ship's route and fueling stops, although specifics on the fuel type, origin, and quality are not available.

The Patapsco River ( pə-TAP-skoh ) mainstem is a 39-mile (63 km) river in central Maryland that flows into the Chesapeake Bay. The river's tidal portion forms the harbor for the city of Baltimore. With its South Branch, the Patapsco forms the northern border of Howard County, Maryland. The name "Patapsco" is derived from the Algonquian pota-psk-ut, which translates to "backwater" or "tide covered with froth".





NY Post
Washington Post

Yahoo! News

Yahoo! News

ABC News

James Gordon

By LEA SKENE

NBC

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

Wikipedia

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

Wikipedia

PANORA

Wikipedia

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

PANORA

Wikipedia

Wikipedia

PANORA

Wikipedia